Background
If you're building a feature like a digital integrity pact, certificate, scholarship request. that sends emails asynchronously when users click submit, then Laravel queue workers are your best friends.
But here's the thing: in production, you can't just run php artisan queue:work in your terminal and call it a day.
Close that terminal window, and boom — your queue dies, and your emails won't be sent.
That's where Supervisor comes in.
It keeps your Laravel queue workers alive and running 24/7, even after server reboots. Here's how to set it up the right way.
So Today we'll walk through setting up Supervisor to manage your Laravel queue workers on a Linux server.
1. Check Your Linux Distro
First, figure out which Linux distro you're running. Use one of these:
lsb_release -a
# or
cat /etc/os-release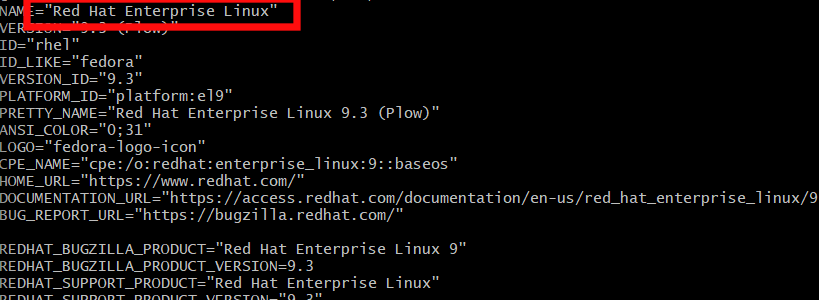
2. Install Supervisor (for RHEL/CentOS)
Using Ubuntu/Debian? Just replace
yumwithapt.
For Documentation just check Supervisor Documentation.
Switch to the root user:
sudo su Then install Supervisor:
yum install supervisor -yEnable and start the Supervisor service:
systemctl enable supervisord
systemctl start supervisordVerify that Supervisor is running:
systemctl status supervisord3. Configure Supervisor for Laravel
Make sure your .env has this seeting:
QUEUE_CONNECTION=database
also make sure your job table is created: if not run:
php artisan queue:table
php artisan migrate4. Create a Supervisor Configuration File
Head to the Supervisor config directory:
cd /etc/supervisord.d
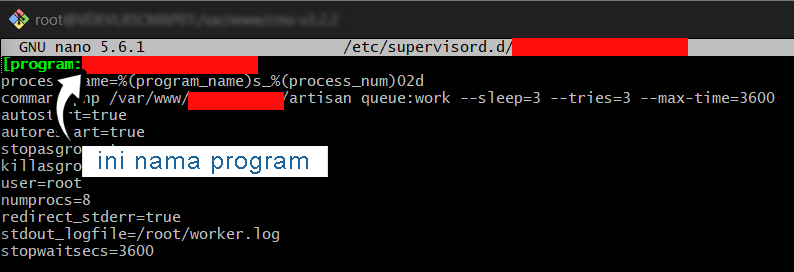
nano laravel-queue.ini #ini adalah membuat file baru di folder tersebutPaste this configuration:
[program:laravel-queue]
process_name=%(program_name)s_%(process_num)02d
command=php /path/to/your/app/artisan queue:work --sleep=3 --tries=3 --timeout=90
autostart=true
autorestart=true
stopasgroup=true
killasgroup=true
user=root
numprocs=8
redirect_stderr=true
stdout_logfile=/root/worker.log
stopwaitsecs=3600Replace
/path/to/your/appwith the actual path to your Laravel application.
5. Launch it
Once saved, tell Supervisor to reload and start the new program:
supervisorctl reread
supervisorctl update
supervisorctl start laravel-queuemake sure to replace
laravel-queuewith the name you used in your config file.
6. Check the Status
To see if your queue workers are running, use:
supervisorctl statusor if you need to debug
cat /root/worker.logAnd thats it ! Your Laravel queue workers are now managed by Supervisor, ensuring they stay alive and kicking even if your server reboots or the terminal closes.
